Hi there!
This guide explains how to integrate your custom Add-On with TreeCapitator using Minecraft’s scriptevent system. By following these instructions, you can register your custom trees and axes, allowing them to work seamlessly with TreeCapitator’s tree-cutting functionality!
Really nothing too complicated, but make sure you read everything! ^^
Basic Add-On Registration
For most add-ons with a small to moderate number of trees and axes, you can use a single registration command.
Add-On Configuration
To register your Add-On with TreeCapitator, use the script event treecapitator:register_addon with a JSON payload containing your add-on details:
interface Addon {
name: string;
enabled?: boolean; // Optional, defaults to true
item_check?: string; // Optional, if enabled is false, TreeCapitator will check if this item exists before enabling the integration
on_load?: string; // Optional command to run after registration
trees?: Tree[];
axes?: Axe[];
}
Here’s what each field means:
| Field | Type | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| name | string | The name of your add-on | ✔️ |
| enabled | boolean | Whether the add-on is enabled by default. Defaults to true, you usually don’t need to change this. | ❌ |
| item_check | string | Item ID to check if your add-on is installed. If enabled is set to false, TreeCapitator will check if this item exists before enabling the integration. | ❌ |
| on_load | string | Command to run after successful registration | ❌ |
| trees | Tree[] | Array of tree definitions | ❌ |
| axes | Axe[] | Array of axe definitions | ❌ |
Simple Example
Here’s a minimal example with just one tree and one axe:
// Register a simple add-on with one tree and one axe
world.afterEvents.worldInitialize.subscribe(() => {
const simpleAddon = {
name: "Simple Tree Add-On",
trees: [
{
id: "simple:maple_log",
leaves: {
types: ["simple:maple_leaves"],
range: 6,
sides_required: 3
},
shape: {
log_up_diagonal: true
}
}
],
axes: [
{ id: "simple:maple_axe" }
],
on_load: "say Simple Tree Add-On registered with TreeCapitator!"
};
world.getDimension("overworld").runCommand(
"scriptevent treecapitator:register_addon " + JSON.stringify(simpleAddon)
);
});
Complete Example
For slightly more complex add-ons, here’s a more detailed example:
// Define your addon configuration
const myAddon = {
name: "My Nature Add-On",
trees: [
{
id: "mynature:rainbow_log",
nether: false,
variants: ["mynature:rainbow_wood"],
leaves: {
types: ["mynature:red_leaves", "mynature:green_leaves", "mynature:blue_leaves"],
range: 7,
sides_required: 4,
},
shape: {
leaf_diagonal: true,
log_up_diagonal: true,
log_up_diagonal_side: true,
max_branch: 3,
},
},
],
axes: [
{ id: "mynature:stone_axe" },
{ id: "mynature:diamond_axe", lang: "My super cool diamond axe" },
],
on_load: "say TreeCapitator Compatibility Added!",
};
// Register the addon after the world initializes
world.afterEvents.worldInitialize.subscribe(() => {
world.getDimension("overworld").runCommand(
"scriptevent treecapitator:register_addon " + JSON.stringify(myAddon)
);
});
Once registered, your axes and logs will show up in TreeCapitator! 🎉
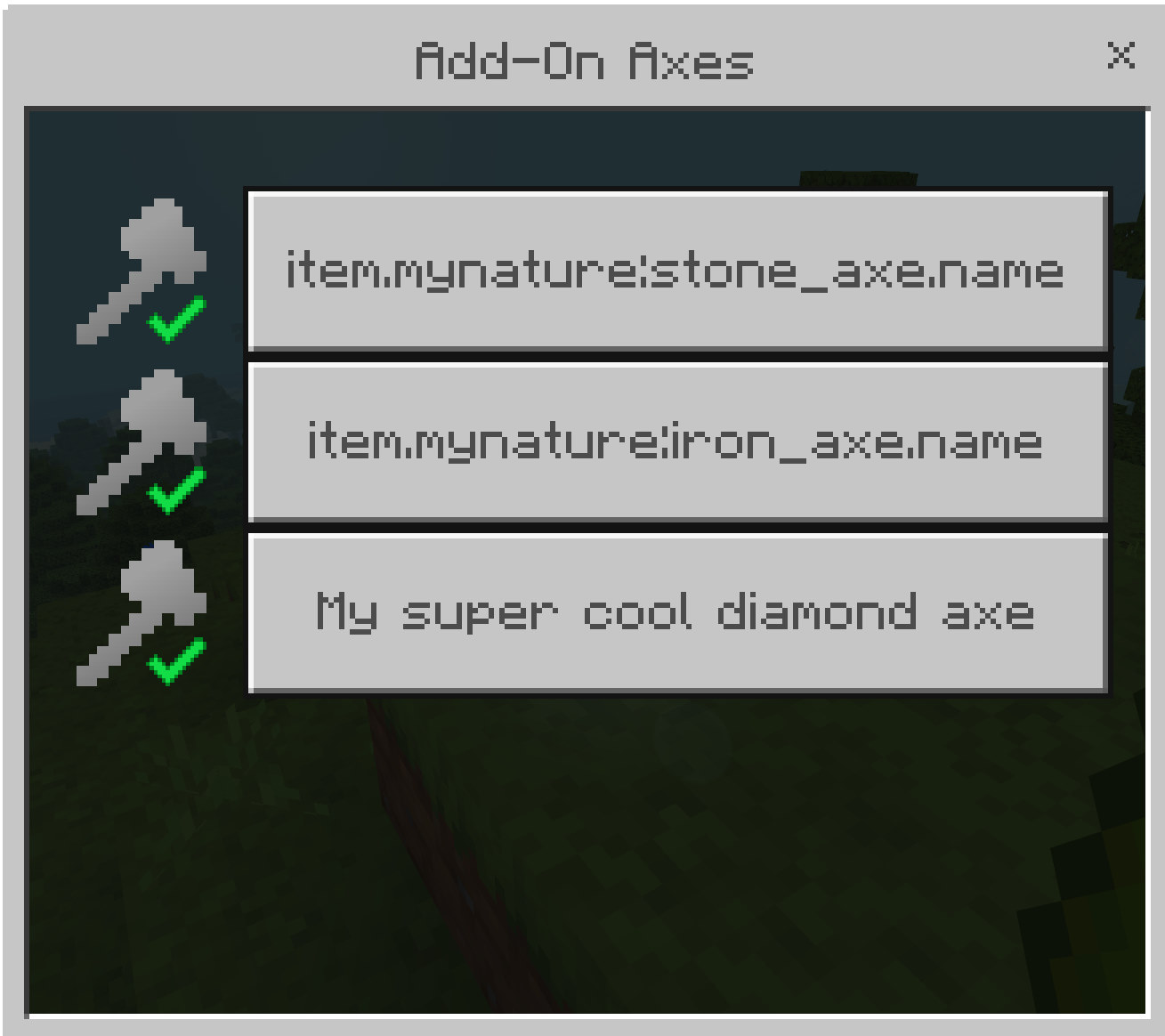
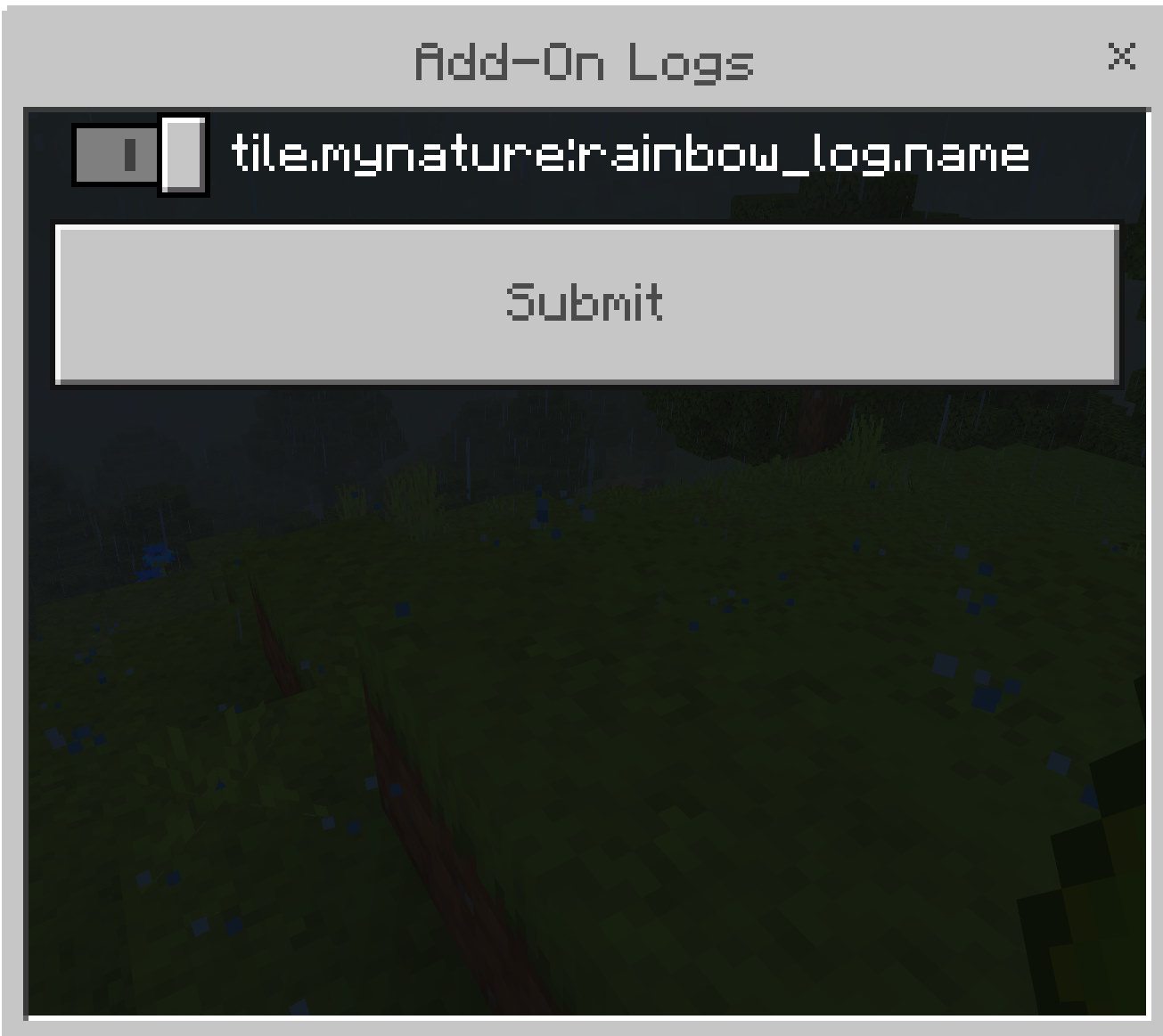
Advanced: Multi-Step Registration for Larger Add-Ons
If your add-on has many trees or axes, you might hit the 2000 character limit of script events. In this case, you’ll need to split your registration into multiple steps using these script events:
treecapitator:register_addon- Register the add-on and its basic informationtreecapitator:add_trees- Add trees to the already registered add-ontreecapitator:add_axes- Add axes to the already registered add-on
Multi-Step Registration Example
import { world } from "@minecraft/server";
// First, register the basic addon information
function registerMyAddon() {
// Step 1: Register the base addon (without trees or axes)
const baseAddon = {
name: "My Nature Add-On",
item_check: "mynature:guide_book",
on_load: "say Registration started!"
};
world.getDimension("overworld").runCommand(
`scriptevent treecapitator:register_addon ${JSON.stringify(baseAddon)}`
);
// Step 2: Add trees in batches
registerTreeBatch1();
registerTreeBatch2();
// Step 3: Add axes
registerAxes();
}
// First batch of trees
function registerTreeBatch1() {
const treeBatch1 = {
addonName: "My Nature Add-On", // Must match name used during registration
trees: [
{
id: "mynature:rainbow_log",
leaves: {
types: ["mynature:red_leaves", "mynature:yellow_leaves"],
range: 7,
sides_required: 4,
},
shape: {
log_up_diagonal: true,
log_up_diagonal_side: true,
max_branch: 3,
leaf_diagonal: true,
},
},
{
id: "mynature:ancient_oak_log",
variants: ["mynature:ancient_oak_wood"],
leaves: {
types: ["mynature:ancient_oak_leaves"],
range: 9,
sides_required: 3,
},
shape: {
log_up_diagonal: true,
max_branch: 4,
leaf_diagonal: true,
},
},
]
};
world.getDimension("overworld").runCommand(
`scriptevent treecapitator:add_trees ${JSON.stringify(treeBatch1)}`
);
}
// Second batch of trees
function registerTreeBatch2() {
const treeBatch2 = {
addonName: "My Nature Add-On",
trees: [
{
id: "mynature:blue_mahogany_log",
leaves: {
types: ["mynature:blue_mahogany_leaves"],
range: 6,
sides_required: 3,
},
shape: {
leaf_diagonal: true,
log_up_diagonal: true,
max_branch: 2,
},
}
]
};
world.getDimension("overworld").runCommand(
`scriptevent treecapitator:add_trees ${JSON.stringify(treeBatch2)}`
);
}
// Register axes
function registerAxes() {
const axesBatch = {
addonName: "My Nature Add-On",
axes: [
{ id: "mynature:stone_axe" },
{ id: "mynature:iron_axe" },
{ id: "mynature:diamond_axe", lang: "My super cool diamond axe" }
]
};
world.getDimension("overworld").runCommand(
`scriptevent treecapitator:add_axes ${JSON.stringify(axesBatch)}`
);
}
// Register everything when the world initializes
world.afterEvents.worldInitialize.subscribe(() => {
registerMyAddon();
});
Tree and Axe Configuration
Tree Configuration
When defining custom trees, you need to provide a Tree object with the following structure:
interface Tree {
id: string;
lang?: string;
nether?: boolean;
variants?: string[];
leaves: {
types: string[];
persistent_state?: string;
range: number;
sides_required: number;
};
shape: {
stem?: boolean;
leaf_diagonal?: boolean;
log_up_diagonal?: boolean;
log_up_diagonal_side?: boolean;
max_branch?: number;
};
}
Here’s what each field means:
| Field | Type | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| id | string | The unique identifier for the tree log | ✔️ |
| lang | string | The language key for the tree name (defaults to tile.${id}.name). Can also be a normal string. |
❌ |
| nether | boolean | Whether this is a Nether tree. Nether trees have a custom leaf decay option. | ❌ |
| variants | string[] | Alternative log types (e.g. a mossy log variant) | ❌ |
| leaves.types | string[] | Block IDs for leaves associated with this tree | ✔️ |
| leaves.persistent_state | string | Block state to check for leaf persistence | ❌ |
| leaves.range | number | Maximum distance to search for leaves from the trunk. Works similarly to how vanilla tree distance works. | ✔️ |
| leaves.sides_required | number | Minimum number of sides with leaves to be considered a valid tree. This is NOT leaf count. Range from 1-5, as TreeCapitator will check leaves in north, east, west, south and up direction) | ✔️ |
| shape.stem | boolean | Whether this tree has a 2x2 stem (like giant jungle trees) | ❌ |
| shape.leaf_diagonal | boolean | Whether leaves connect diagonally | ❌ |
| shape.log_up_diagonal | boolean | Whether tree logs connect diagonally upwards | ❌ |
| shape.log_up_diagonal_side | boolean | Whether logs connect diagonally upwards AND sideways | ❌ |
| shape.max_branch | number | Maximum horizontal branch length. Set this if you have tree branches going sideways. | ❌ |
Axe Configuration
When defining custom axes, you can specify the following properties:
| Property | Type | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| id | string | The unique identifier for the axe | ✔️ |
| lang | string | The language key for the axe name (defaults to item.${id}.name). You can also pass a normal string here. |
❌ |
Overwriting Vanilla Trees
TreeCapitator supports overwriting vanilla Minecraft trees with custom configurations! This powerful feature allows you to modify how TreeCapitator interacts with default Minecraft trees.
Vanilla Tree Overwrite Configuration
To overwrite vanilla trees, use the script event treecapitator:overwrite_trees with a JSON payload containing the tree IDs as keys and partial tree configurations as values:
// Example payload structure
{
"minecraft:oak_log": {
"leaves": {
"range": 8,
"sides_required": 2
},
"shape": {
"log_up_diagonal": true,
"max_branch": 3
}
},
"minecraft:birch_log": {
"leaves": {
"sides_required": 3
},
"shape": {
"leaf_diagonal": true
}
}
}
The system uses a deep merge approach, where only the specified properties are overwritten, and the rest remain unchanged.
Example: Overwriting Vanilla Oak Trees
Here’s an example of how to overwrite vanilla oak trees with a custom configuration:
// Overwrite vanilla oak trees with enhanced properties
world.afterEvents.worldInitialize.subscribe(() => {
const oakOverwrite = {
"minecraft:oak_log": {
"leaves": {
"range": 8, // Increased from default
"sides_required": 2 // Reduced from default
},
"shape": {
"log_up_diagonal": true,
"max_branch": 3 // Increased branch detection
}
}
};
world.getDimension("overworld").runCommand(
"scriptevent treecapitator:overwrite_trees " + JSON.stringify(oakOverwrite)
);
});
Multi-Tree Overwrite Example
You can overwrite multiple vanilla trees in a single command:
// Overwrite multiple vanilla trees
world.afterEvents.worldInitialize.subscribe(() => {
const treeOverwrites = {
"minecraft:oak_log": {
"leaves": {
"range": 7,
"sides_required": 2
},
"shape": {
"log_up_diagonal": true,
"max_branch": 3
}
},
"minecraft:birch_log": {
"leaves": {
"sides_required": 3
},
"shape": {
"log_up_diagonal": true
}
},
"minecraft:spruce_log": {
"leaves": {
"range": 8,
"sides_required": 3
},
"shape": {
"leaf_diagonal": true,
"log_up_diagonal": true
}
}
};
world.getDimension("overworld").runCommand(
"scriptevent treecapitator:overwrite_trees " + JSON.stringify(treeOverwrites)
);
});
Overwritable Properties
You can overwrite any property of the Tree interface. Common properties to overwrite include:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| leaves.range | Maximum distance to search for leaves from the trunk |
| leaves.sides_required | Minimum number of sides with leaves to be considered a valid tree |
| leaves.types | Block IDs for leaves associated with this tree |
| shape.leaf_diagonal | Whether leaves connect diagonally |
| shape.log_up_diagonal | Whether tree logs connect diagonally upwards |
| shape.log_up_diagonal_side | Whether logs connect diagonally upwards AND sideways |
| shape.max_branch | Maximum horizontal branch length |
| variants | Alternative log types (e.g. a mossy log variant) |
Important Notes and Limitations
- When overwriting vanilla trees, you must use the correct Minecraft IDs for logs (e.g.,
minecraft:oak_log). - Only specify the properties you want to change - other properties will retain their default values.
- Overwriting vanilla trees affects all instances of that tree type in the world.
- This feature is compatible with both the Basic and Multi-Step registration methods.
- Keep the 2000 character limit in mind. You can call the
treecapitator:overwrite_treesscriptevent multiple times.
Supported Vanilla Tree Types
TreeCapitator supports overwriting all vanilla Minecraft tree types:
| Tree Type | Log Block ID |
|---|---|
| Oak | minecraft:oak_log |
| Birch | minecraft:birch_log |
| Spruce | minecraft:spruce_log |
| Jungle | minecraft:jungle_log |
| Acacia | minecraft:acacia_log |
| Dark Oak | minecraft:dark_oak_log |
| Mangrove | minecraft:mangrove_log |
| Cherry | minecraft:cherry_log |
| Pale Oak | minecraft:pale_oak_log |
| Crimson | minecraft:crimson_stem |
| Warped | minecraft:warped_stem |
Best Practices
- Use unique identifiers for your trees and axes to avoid conflicts with other Add-Ons.
- For larger add-ons, split your registration into multiple steps to stay under the 2000 character limit.
- When using multi-step registration, make sure the
addonNamematches exactly in all registration steps. - Optimize your trees as much as possible. For example, if your trees don’t have horizontal branches, don’t set
max_branch. - Test your integration thoroughly to ensure all trees and axes work as expected with TreeCapitator.
- Enable Trunk Outline in TreeCapitator’s settings to easily test your integration.
- When overwriting vanilla trees, consider the impact on gameplay and balance. Adjust parameters carefully.
By following this guide, you can seamlessly integrate your custom Add-On with TreeCapitator, allowing players to enjoy your custom trees and axes with the tree-cutting functionality provided by TreeCapitator.